FTTN internet vs Cable

January 30 2024 · 5 minutes to read
FTTN and Cable internet differ in how they deliver internet services: FTTN uses a combination of fiber optic cables and copper wires, while Cable relies on coaxial cables.
Availability and infrastructure vary depending on location, which can impact the choice of internet service technologies.
Assess your internet usage, check service availability, and compare plans to choose the best internet option for your needs and budget.
When it comes to choosing the perfect internet service for your home, the options can be overwhelming. With a myriad of technologies like Fiber Optics, Cable, DSL, LTE, Satellite, and Broadband, how can you be sure you're making the right decision? Among these options, you may have stumbled upon FTTN and wondered how it compares to Cable Internet.
In this comprehensive guide, we'll dive deep into the world of FTTN and Cable Internet, exploring their pros and cons, to help you make an informed choice that best suits your needs and lifestyle. Get ready to demystify these internet technologies and discover the ideal solution for your home's internet access.
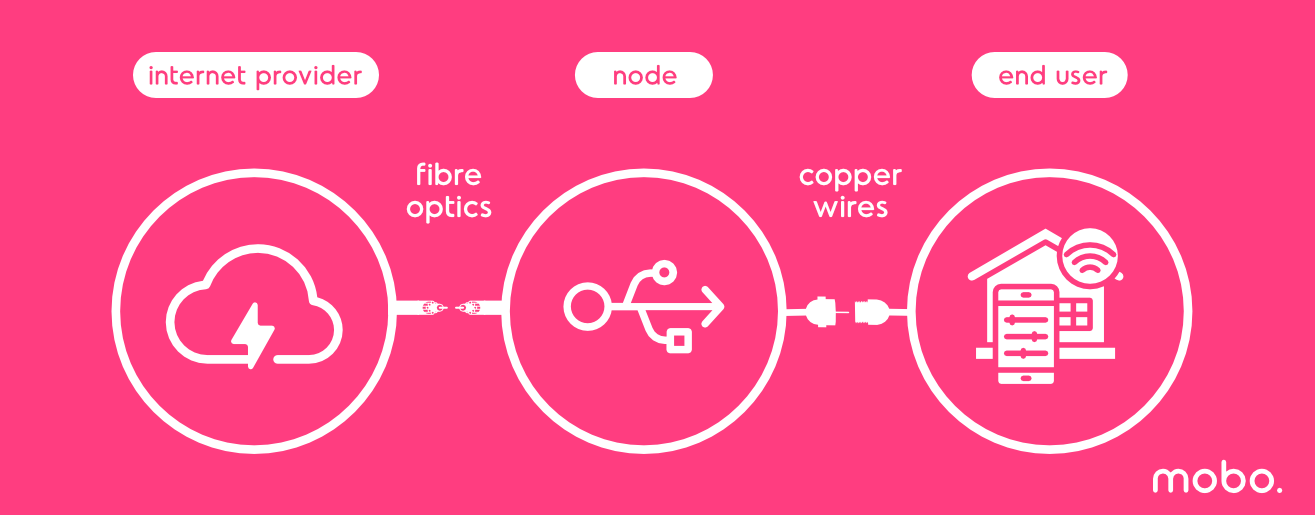
As you can guess, FTTN stands for Fibre to the Node or Neighbourhood, but what does it mean ? Very simplistic answer is that it's the way the internet connection is delivered to your modem or wifi router. Signal in FTTN connection is transported via Fibre Optics cable up until your neighbourhood, then goes through a copper wire in your house.
Usually fiber optic is faster and more stable than cable. Unfortunately, only 35% of Canadian households had access to Fiber internet (FTTH) with 11% subscribing according to a 2018 survey.
*Source: 2018 survey from cansumer.ca
Cable television is available to Canadian since 1950. 40 years later the internet was able to travel through those same copper wires. Similar to the television signal going through the coaxial cables, internet can reach your home at a much greater speed than the phone line.
DSL (Digital Subscriber Line) on the other hand use phone wires for internet transmission.
The speed of cable internet varies according to different factors. You may consider your location, the service provider the usage in your neighbourhood and atmospheric interference.


Which technology is right for you?
Now that you know more about the difference between Cable Internet and FTTN, can you make the right choice? Getting the right high-speed internet connection is not an easy task because different factors are to consider. The main points to consider are the available bandwidth, your data usage and the different plans available in your area.
| Factor | Description | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Bandwidth Requirements | The amount of data that can be transmitted over an internet connection at a given time. | Higher bandwidth is necessary for activities like streaming, gaming, and video conferencing. |
| Data Usage and Plan Options | The amount of data you consume on a monthly basis and the available plans that cater to your needs. | Choose a plan that offers sufficient data and speed at an affordable price. |
| Location and Infrastructure Availability | The availability of internet service technologies in your area and the quality of the infrastructure. | Some areas may have limited options, so choose the best available technology based on your location. |
| Technology | Download speed range | Upload speed range | Availability | Prices |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DSL | 5-35 Mbps | 1-10 Mbps | High | |
| Cable | 10-500 Mbps | 5-50 Mbps | Moderate | |
| LTE | 5-30 Mbps | 2-5 Mbps | Moderate | |
| Satellite | 5-25 Mbps | 1 Mbps | Very high | |
| FTTN | 50 Mbps - 200 Mbps | 10 Mbps - 50 Mbps | Low | |
| FTTH | 250-1000 Mbps | 250-1000 Mbps | Very low |
The Johnson family been using a basic DSL connection for years. With two teenagers and both parents working from home, they've noticed their internet connection is struggling to keep up with the increased demand. The family needs a better internet service that can handle multiple devices streaming, gaming, and video conferencing simultaneously.
The Johnsons make a list of their internet activities and estimate the required bandwidth for each. They realize they need a minimum download speed of 100 Mbps and an upload speed of 20 Mbps to accommodate their usage.
The Johnsons research various internet service providers (ISPs) in their area and discover that they have access to cable, FTTN, and FTTH options.
The Johnsons compare the available plans from different ISPs, considering the download and upload speeds, data limits, and pricing. They find that the FTTH option provides the best performance, but it's quite expensive. On the other hand, cable and FTTN options offer more affordable plans with speeds that meet their requirements.
After considering all factors, the Johnsons decide to go for an FTTN plan with a download speed of 150 Mbps and an upload speed of 30 Mbps. This plan offers a good balance between performance and cost, meeting their needs without breaking the bank.
In conclusion, understanding the differences between FTTN and Cable internet technologies is essential for making an informed decision about the best internet plan for your needs. By assessing your internet usage, checking the availability of service providers in your area, and comparing plans, you can confidently choose the right internet service that suits your requirements and budget.
Explore the key differences between Starlink's Standard and High Performance dishes to determine...
Are you planning a move or want to change internet operator? We've rounded up the key points to make the transition hassle-free.
How to improve your internet speed. Tips for optimizing Wi-Fi, measuring speed, and getting the most out of your internet!
4.7/5 out of 207 reviews